Asynchronous Programming With CompletableFuture
RELATED POST
들어가면서
CompletableFuture is part of Java’s java. util. concurrent package and provides a way to write asynchronous code by representing a future result that will eventually appear. It lets us perform operations like calculation, transformation, and action on the result without blocking the main thread.
CompleableFuture는 Java의 java.util. 동시 패키지의 일부이며, 나중에 나타날 미래 결과를 표현하여 비동기 코드를 작성하는 방법을 제공합니다. 이를 통해 메인 스레드를 차단하지 않고도 결과에 대한 계산, 변환 및 작업과 같은 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
Future
- Java5에 추가된 Future는 비동기 작업의 결과를 나타내는 Interface
-
작업이 아직 완료되지 않았더라도 결과에 접근할 수 있는 방법을 제공
-
Code
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; @Slf4j public class FutureExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); Future<String> future = executor.submit(()-> { Thread.sleep(5000); return "task complete"; } ); log.info("wait until Future gets complete result"); log.info(future.get()); executor.shutdown(); } }

- future.get()은 blocking call이라서 future.get() 이후의 작업은 비동기 처리 결과를 얻고 나서 진행된다.
-
Limitation
- 비동기 작업 실행
- 작업 콜백
- 작업 조합
- 예외 처리
-
Solution
- Java8에서 지원하는 CompletableFuture의 특징들을 통해 Future을 이용해서 처리 하기 힘든 비동기 프로그래밍을 처리해보고자 합니다.
- 비동기 메서드 체이닝 : 비동기 메서드 체이닝을 통해 여러 작업을 연결하여 실행할 수 있다.
- 콜백 지원 : 콜백 메서드를 등록하여 작업이 완료되었을 때 특정 동작을 수행할 수 있다.
- 조합성 개선 : CompletableFuture를 조합하고 결합하여 더 복잡한 비동기 흐름을 만들 수 있다.
- 에러 처리 개선
- Java8에서 지원하는 CompletableFuture의 특징들을 통해 Future을 이용해서 처리 하기 힘든 비동기 프로그래밍을 처리해보고자 합니다.
With/Without Return Type
- CompleteableFuture가 제공하는 비동기 작업 실행
- runAsync
- 반환 값이 없는 경우
- 비동기로 작업 실행 call
- supplyAsync
- 반환 값이 있는 경우
- 비동기로 작업 실행 call
-
CompletableFuture.java(java.util.concurrent)
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> { //supplyAsync public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) { return asyncSupplyStage(ASYNC_POOL, supplier); } public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor) { return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier); } //runAsync public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) { return asyncRunStage(ASYNC_POOL, runnable); } public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) { return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable); } } -
Example
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.*; @Slf4j public class CompletableFutureReturnExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CompletableFuture<Void> runAsyncFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { log.info("runAsync with Thread : " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); }); log.info("After runAsyncFuture"); CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsyncFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return "Task Complete"; }); log.info("Before SupplyAsyncFuture Result"); log.info(supplyAsyncFuture.get()); log.info("After SupplyAsyncFuture Result"); } }

-
Result
- runAsync/supplyAsync는 Java7에 추가된 ForkJoinPool의 commonPool()을 사용해 작업을 실행할 Thread를 ThreadPool로부터 얻어 실행
- 만약 원하는 ThreadPool을 사용하려면 ExecutorService를 Parameter로 넘겨 주면 된다.
- get()을 하더라도 결과가 나올 때까지 blocking을 하고 있지 않음(비동기 작업 실행)
- runAsync/supplyAsync는 Java7에 추가된 ForkJoinPool의 commonPool()을 사용해 작업을 실행할 Thread를 ThreadPool로부터 얻어 실행
Asynchronous Method Chaining
- thenApply
- 반환 값을 받아서 다른 값을 반환함
- parameter : 함수형 인터페이스 Function
- thenAccept
- 반환 값을 받아 처리하고 값을 반환하지 않음
- parameter : 함수형 인터페이스 Consumer
- thenRun
- 반환 값을 받지 않고 다른 작업을 실행함
- parameter : 함수형 인터페이스 Runnable
-
CompletableFuture.java(java.util.concurrent)
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> { public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) { return uniApplyStage(null, fn); } public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) { return uniAcceptStage(null, action); } public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) { return uniRunStage(null, action); } } -
Example
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; @Slf4j public class CompletableFutureChainingExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> { log.info("supplyAsync with Thread : "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); return "first return data"; }) .thenApply(s -> { log.info("thenApply with Thread : "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); return s.toUpperCase(); }) .thenAccept(a -> { log.info("thenAccept with Thread : "+ Thread.currentThread().getName()); log.info(a); }); log.info("Main Thread : "+Thread.currentThread().getName()); } }

-
Result
- runAsync/supplyAsync를 사용했기 때문에 Thread를 ThreadPool로부터 얻어 실행
- ForkJoinPool의 commonPool()
- thenApply/thenAccept/thenRun은 callback값 및 return의 여부에 따라 적절하게 조합해서 이용하면 된다.
- CompletableFuture의 완벽한 결과가 나오기 전에 마지막 log문이 실행된 것을 볼 수 있다.(Asynchronous Programming)
- runAsync/supplyAsync를 사용했기 때문에 Thread를 ThreadPool로부터 얻어 실행
Combination in CompletableFuture
- thenCompose
- 두 작업이 이어서 실행하도록 조합하고 압선 작업의 결과를 받아서 Callback 실행
- parameter : 함수형 인터페이스 Function
- thenCombine
- 두 작업을 독립적으로 실행하고 모두 완료되었을 때 Callback 실행
- parameter : 함수형 인터페이스 Function
- allOf
- 여러 작업들을 동시에 실행하고 모든 작업 결과에 Callback 실행
- anyOf
- 여러 작업들 중에서 가장 빨리 끝난 하나의 결과에 Callback 실행
-
CompletableFuture.java(java.util.concurrent)
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> { public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) { return uniComposeStage(null, fn); } public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) { return biApplyStage(null, other, fn); } public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) { return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1); } public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) { int n; Object r; if ((n = cfs.length) <= 1) return (n == 0) ? new CompletableFuture<Object>() : uniCopyStage(cfs[0]); for (CompletableFuture<?> cf : cfs) if ((r = cf.result) != null) return new CompletableFuture<Object>(encodeRelay(r)); cfs = cfs.clone(); CompletableFuture<Object> d = new CompletableFuture<>(); for (CompletableFuture<?> cf : cfs) cf.unipush(new AnyOf(d, cf, cfs)); if (d.result != null) for (int i = 0, len = cfs.length; i < len; i++) if (cfs[i].result != null) for (i++; i < len; i++) if (cfs[i].result == null) cfs[i].cleanStack(); return d; } } -
Example
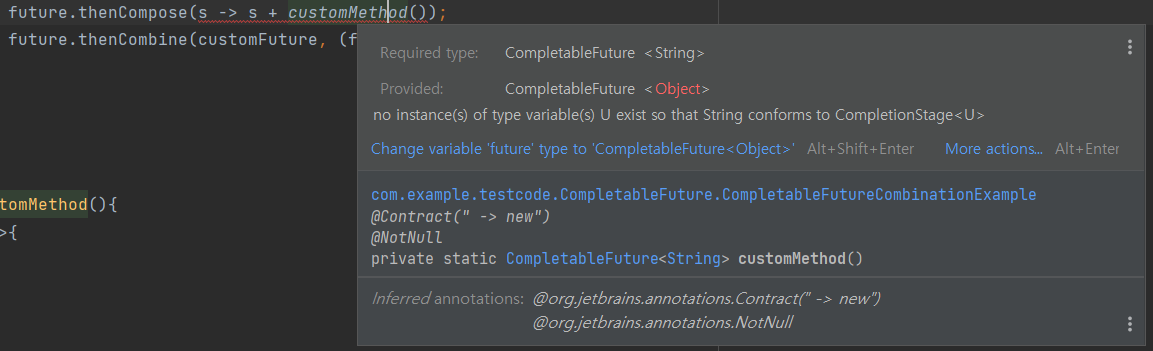
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; @Slf4j public class CompletableFutureCombinationExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> { return "CompletableFutureExample with "; }); CompletableFuture<String> customFuture = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> { return "thenCombine"; }); CompletableFuture<String> finalFuture1 = future.thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.completedFuture(s + customMethod())); CompletableFuture<String> finalFuture2 = future.thenCombine(customFuture, (f1, f2) -> f1 + f2); log.info(finalFuture1.get()); log.info(finalFuture2.get()); } }

-
Result
- thenCombine은 두 작업을 독립적으로 실행하고 모두 완료되었을 경우 콜백을 실행한다.
- thenCompose는 두 작업을 이어서 실행하고 앞선 작업의 결과를 받아서 사용한다.
- CompletableFuture.java의 thenCompose 메소드 Parameter
- Function에 T타입 -> U타입으로 변환할 떄 CompletionStage 타입으로만 변환을 해야한다.(CompletableFuture 타입으로 그대로 사용 시 IDE에서 컴파일 에러 발생)
- CompletedFuture 메서드로 새로운 CompletableFuture 객체를 생성해야한다.

ExceptionHandling in CompletableFuture
- exceptionally
- 발생한 error를 받아서 에외 처리 가능
- parameter : 함수형 인터페이스 Function
- handle, handleAsync
- 결과값, error를 받아서 에러가 발생한 경우 아닌 경우 모두 처리 가능
- parameter : 함수형 인터페이스 BiFunction
-
CompletableFuture.java(java.util.concurrent)
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> { public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn) { return uniExceptionallyStage(null, fn); } public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) { return uniHandleStage(null, fn); } public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) { return uniHandleStage(defaultExecutor(), fn); } public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor) { return uniHandleStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn); } } -
Example
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; @Slf4j public class CompletableFutureCombinationExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture .supplyAsync(() -> { throw new RuntimeException("RuntimeException Error"); }); CompletableFuture<String> exceptionallyFuture = future .exceptionally(e -> { e.getMessage() }); CompletableFuture<String> handleFuture = future .handle((result, e) -> { return e == null ? result : e.getMessage(); }); log.info(exceptionallyFuture.get()); log.info(handleFuture.get()); } }

-
Result
- exceptionally와 handle의 사용은 에러가 발생한 경우만 처리할 것인지 / 에러가 발생한 경우와 아닌 경우 모두를 처리할 것인지에 따라 나뉜다.
Reference
- https://wbluke.tistory.com/50
- https://velog.io/@brucehan/CompletableFuture-%EC%A0%95%EB%A6%AC
- https://sh970901.tistory.com/139
- https://mangkyu.tistory.com/263
- https://velog.io/@suyeon-jin/JAVA-CompletableFuture