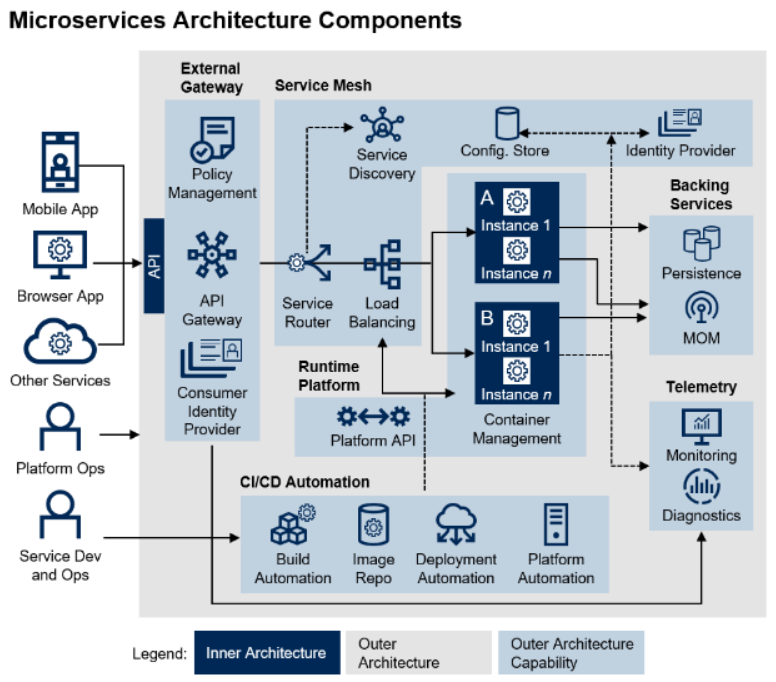
MSA(Microservice Architecture) Components
0. 들어가면서
-
이전 Post에서는 MSA와 MA의 차이와 기본적인 개념에 대해 알아봤습니다. 이번 Post에서는에서는 MSA의 구조 및 구성 요소에 대해 알아보고자 합니다.
-
Microsevice Architecture Components
- Inner Architecture
- Outer Architecture
-
Components Structure

1. Inner Architecture
- 내부의 Service를 어떻게 잘 나눴는지에 대한 설계
- 실제 비즈니스가 실행되는 각 MSA내 구조를 정의한 Architecture
- Business, Service, System마다 각각의 특성이 있기 때문에 표준이 없음
-
MSA 설계시에 가장 어려운 부분
-
1.1 Consideration
-
1.1.1 Service
- Service를 어떻게 정의할 것인가?
- 비즈니스, Service간 종속성, 배포 용이성, 장애 대응, 운영 효율성
-
1.1.2 DB Access
- DB Access 구조를 어떻게 설계할 것인가?
- 각 Service마다 각자의 DB를 사용하는데 각 Service에 연결된 DB의 정합성을 보장할 필요가 있음
-
1.1.3 API
- Service 내 API를 어떻게 설계할 것인가?
-
1.1.4 Layer
- Component들의 Layer는 어떻게 설계할 것인가?
-
2. Outer Architecture
- Components
- External Gateway
- Service Mesh
- Container Manager
- Backing Services
- Telemetry
- CI/CD Automation
-
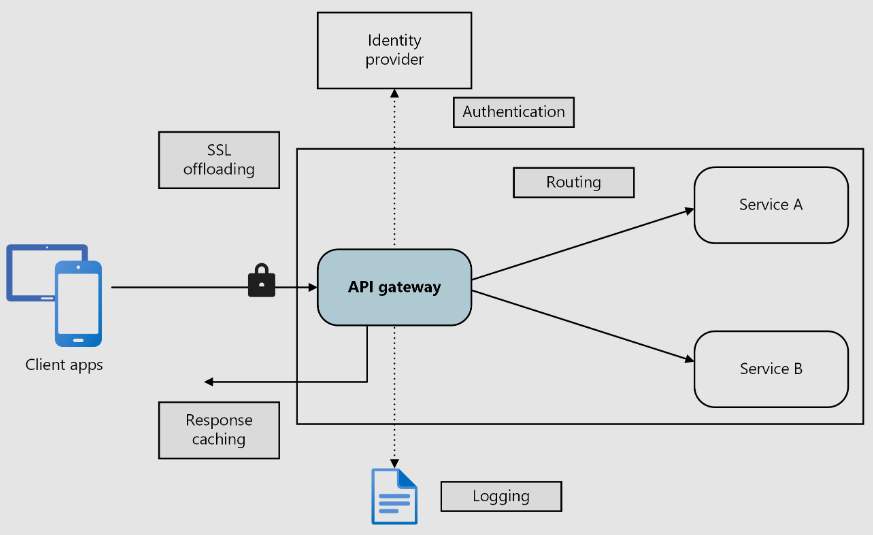
2.1 External Gateway

-
2.1.1 Conception
- 외부로부터 들어오는 접근을 처리하는 부분
- 사용자 인증 및 권한 정책관리를 수행
- API Gateway가 핵심적인 역할 담당
-
2.1.2 API Gateway
- 가장 앞단에 위치하며 모든 API 호출을 받음
- 받은 API 호출을 인증하고 적절한 Service들에 전달(Routing)
-
-
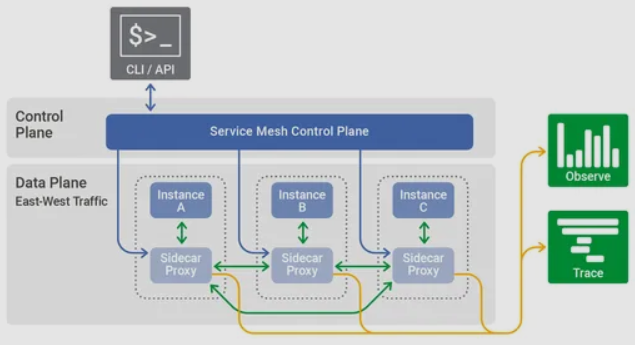
2.2 Service Mesh

-
2.2.1 Conception
- Service간에 네트워크를 제어하는 역할
-
2.2.2 Role
- Service Discovery
- Service Routing
- Failure Recovery
- Load Balancing
- Security
-
2.2.3 API Gateway & Service Mesh
- Position
- API Gateway : Service 그룹 외부 경계
- Servie Mesh : Service 그룹 경계 내부
- Architecture
- API Gateway : 중앙집중형 Architecture(SPOF 생성)
- Servie Mesh : 분산형 Architecture(확장 용이)
- Pattern
- API Gateway : Gateway proxy pattern
- 호출자는 구현 내용을 알 필요 없이 Gateway를 호출하는 방법만 알면 됨
- Servie Mesh : Sidecar proxy pattern
- 호출자의 코드에는 공급자의 주소를 찾는 방법 등 코드가 들어감
- 호출자의 코드는 비즈니스 로직에 내장되는 것이 아닌 sidecar형태로 별개로 관리
- API Gateway : Gateway proxy pattern
- Role :
- API Gateway : 노출되는 부분에 위치하여 내부 서비스 보호 및 제어하는 역할
- Service Mesh : 내부 서비스에 위치하여 서비스를 관리
- Position
-
-
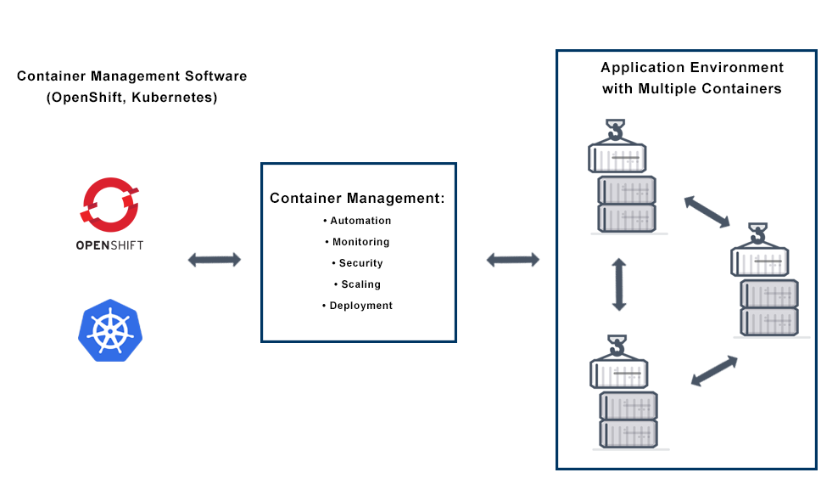
2.3 Container Manager

-
2.3.1 Conception
- Infura Managing
- 컨테이너 기반 Application은 유연성과 자율성을 갖음
- 개발자가 손쉽게 접근 및 운영이 가능해서 MSA에 적합
- Software : Kubernetes, OpenShift,EKS(AWS), GKE(Google Cloud Platform)
- Infura Managing
-
2.3.2 Container Management
- Automation
- Monitoring
- Security
- Scaling
- Deployment
-
-
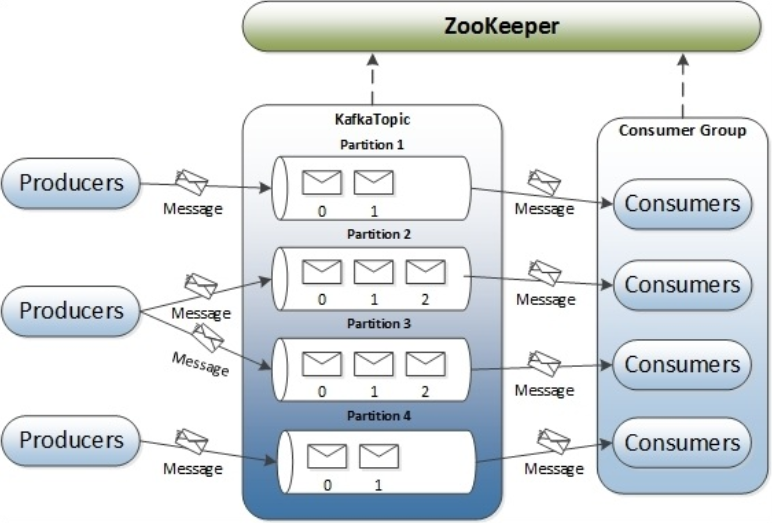
2.4 Backing Services

-
2.4.1 Conception
- Application이 실행되는 중에 네트워크를 통해서 사용할 수 있는 모든 Service
- Attached Resources : Messaging Queue, DB, Cash, SMTP
-
2.4.2 Messaging Queue
- 메세지의 송,수신자가 직접 통신하지 않고 Message Queue를 활용하여 비동기적으로 통신하는 것을 지향
- Data 변경, 보상 Transaction 관련 처리 시에 비동기 처리가 효율적임
- 사용하지 않은 경우
- 여러 Service를 걸친 실시간 Transaction 처리 시에, 특정 Service가 죽어버리면 Transaction은 끊어짐
- 해당 Service 요청을 보존할 수 없고 큰 Error가 발생함
- REST 통신으로 Transaction Failure 처리 구현은 매우 복잡함
- Messaging Queue : Kafka, RabbitMq
-
-
2.5 Telemetry
-
2.5.1 Conception
- 실시간으로 먼 거리에서 원격으로 측정 가능(실시간 원격 성능 측정)
-
2.5.2 Role
- MSA는 분산 환경에서 운영 -> Service들의 상태를 모니터링하고 Service별로 발생하는 이슈들에 대응할 수 있도록 환경 구성함
-
-
2.6 CI/CD Automation
-
2.6.1 Conception
- 지속적인 통합, 전달, 배포를 자동화하여 배포가 잦은 MSA에 꼭 필요한 요소
-
Reference
- https://ksh-coding.tistory.com/136
- https://may9noy.tistory.com/1111
- https://velog.io/@tedigom/MSA-%EC%A0%9C%EB%8C%80%EB%A1%9C-%EC%9D%B4%ED%95%B4%ED%95%98%EA%B8%B0-2-MSA-Outer-Architecure
- https://jeongjin984.github.io/posts/Software-Engineering-MSA/